Young’s Modulus
Young’s Modulus: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Potential Energy of a Stretched Wire, Elastic Potential Energy per Unit Volume of Wire, Spring Analog in Hooke's Law & Increment of Length Due to Own Weight etc.
Important Questions on Young’s Modulus
A student performs an experiment to determine the Young’s modulus of a wire, exactly long, by Searle’s method. In a particular reading, the student measures the extension in the length of the wire to be with an uncertainty of at a load of exactly . The student also measures the diameter of the wire to be with an uncertainty of . Take (exact). The Young’s modulus obtained from the reading is
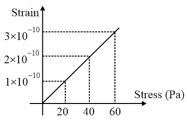
The elastic behaviour of material for linear stress and linear strain, is shown in the figure. The energy density for a linear strain of is _____ . Assume that material is elastic upto the linear strain of .
A steel wire of cross-sectional area can withstand a maximum strain of . Young's modulus of steel is . The maximum mass this wire can hold is,
A light rod of length is suspended from the ceiling horizontally using two vertical wires of equal length tied to its ends. One of the wire is made of steel of crosssectional area sq. cm and young modulus , while the second is made of brass of cross-sectional area sq. . and Young's modulus . Then:
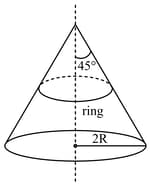
A ring of mass , radius , cross sectional area a and Young's modulus is kept on a smooth cone of radius and semi vertical angle , as shown in the figure. Assume that the extension in the ring is small.
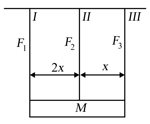
Three vertical wires I,II and III are supporting a block of mass in horizontal position The wires are of equal length and cross-sectional area. It is given that Young's modulus of wire , is and Young's modulus of wire III is and it for wire is . The wires and are attached at extreme ends of the block. If then which of the following are correct [Where and are tension in and wires]
A uniform metal rope of length and area of cross-section is suspended from ceiling vertically. is density and is Young's modulus of material of the wire respectively. Due to its own weight rope sags such the strain energy stored is . Find value of .
A steel wire of diameter and length is clamped firmly at two points A and which are apart and in the same plane. A body is hung from the middle point of the wire such that the middle point sags lower from the original position. The mass of the body is ___ . (Young's modulus of the material of wire is )
A sphere of radius and mass is attached to the lower end of a steel wire of length and diameter . The wire is suspended from high ceiling of the room. When the sphere is made to swing as a simple pendulum, it just grazes the floor at its lowest point. The velocity of the sphere at the lowest position is _____ ( for steel )
A wire of length and cross - sectional area '', made of a material of Young's modulus , is pulled with a constant force on a rough horizontal surface as shown in fig. Then
Imagine a uniform wire of length '' suspended from the ceiling whose young's modulus of elasticity increases linearly from yo at the bottom to yo at the top. If is the area of cross- section and be the load applied at its bottom then (neglect change in area of cross-section).
A copper and a steel wire of same diameter are connected end to end. A deforming force is applied to this composite wire which causes a total elongation of . The two wires will have:
Give any two applications of elastic behaviour of materials and explain them.
Why the maximum height on earth is ? The elastic limit for a typical rock is and the density is about .
Suppose we want to make a crane, which has a lifting capacity of metric tons. How thick should the steel rope be? Mild steel has yield strength of about .
Which of the given metal is not using for making rope for the crane?
Find maximum height of mountain on earth's surface.
The deflection of beams may be decreased by increasing the modulus of_____
The buckling of a beam is found to be more if:
Write two applications of elastic behaviour of the material.
